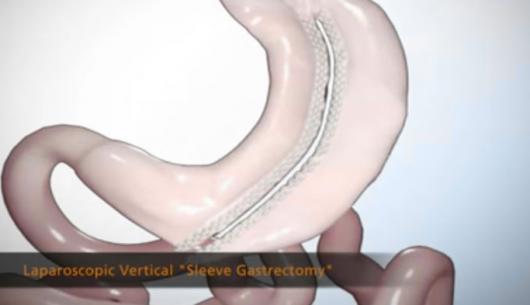
This procedure involves removing a portion of the stomach, leaving patients with a sensation of fullness after eating smaller portions. Scientific studies show a decrease in hunger due to changes in gut hormones (ghrelin and other GI hormones).
Advantages:
- Rapid and significant weight loss
- More weight loss than the adjustable gastric band (approximately 50 – 70 percent excess weight loss)*
- Low risk of “dumping syndrome” – symptoms of weakness, stomach discomfort, and diarrhea after meals
- No foreign objects placed in the body
- No rerouting of the intestines
Compared with Gastric Bypass:
- Lower risk of malabsorption (not getting enough nutrients, vitamins, and minerals in your diet)
- No risk of internal hernia (bowel getting caught in between intestines in the abdomen)
- Lower risk of bowel obstruction, ulcers, and other problems
Disadvantages:
- Not reversible.
- May not be appropriate for patients with reflux disease.
About the Procedure
*This is not an absolute number or guarantee of expected weight loss. Patients may lose more or less weight depending on their individual circumstances. The patient's own efforts (such as eating a healthy diet and making positive lifestyle and behavior changes) will also impact how much weight is lost after any bariatric procedure and whether any weight is regained in the long-term.